With the advancement of mass production and commercialization of humanoid robots, the Advanced Robot Industry Research Institute (GGII) predicts that by 2030, the global force sensor market size in the humanoid robot field will reach 32.806 billion yuan. Of which six-dimensional force sensors in the humanoid robot field will The market size will reach 13.840 billion yuan.
Perception is the prerequisite for humanoid robot control and execution. The sensors in the perception layer are the bridge between software control and hardware components, the interface between the physical world and the digital world, and the key to realizing embodied intelligence.
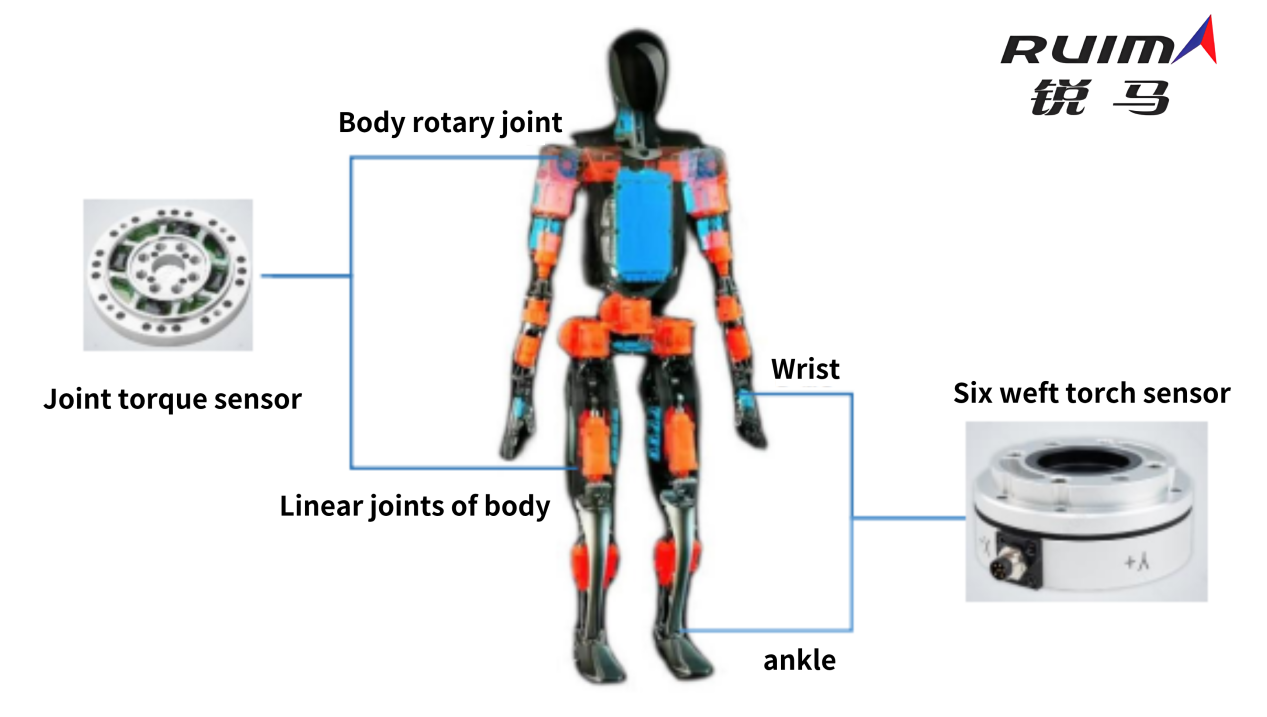
As one type, force sensors are responsible for converting the magnitude of force into relevant electrical signals and can detect mechanical quantities such as tension, pressure, weight, torque, strain and internal stress. Humanoid robots commonly use the highest-dimensional torque sensor - a six-dimensional force sensor (also known as a six-dimensional torque sensor). Six-dimensional force sensors can provide the most comprehensive force sense information. At the same time, they have relatively high technical barriers in areas such as all-round mechanical overload protection and dynamic performance.
The interaction force between the workpiece and the workpiece is sensed through a six-dimensional force sensor, and the sensed force signal is fed back to the control system. The control system then adjusts the movement trajectory and strength of the humanoid robot based on the sensed force signal, thereby achieving force control. precise control.
In fact, the industry is still exploring which technical route of six-dimensional force sensors is more suitable for humanoid robots.
"Who" is more suitable?
Exploration of technical routes
According to different sensing elements, six-dimensional force sensors are mainly divided into strain gauge type, optical type, piezoelectric type, capacitive type, MEMS silicon principle and other principles.
The most mature technology and widely used in the market is the strain gauge type. The strain gauge type usually uses silicon strain gauges or metal foils. The essence is that the material itself deforms, which is then converted into a change in resistance. It has the characteristics of high precision, wide measurement range, low cost, and good high-frequency response characteristics.
So, is the strain gauge type the most suitable six-dimensional force sensor for humanoid robots?
"The strain-gage six-dimensional force sensor can meet the application needs of humanoid robot wrists, but for ankles, it seems a little inadequate and is not the most suitable technical route."Wu Hao, chairman of Ruima Sensors, said during a survey by Gaogong Robot.
The main problem with the strain gauge type is insufficient long-term reliability. Since the strain gauge type is a glue-pasted process, the six-dimensional force sensor using this technical route cannot avoid problems such as zero-point drift, temperature drift, and creep after the oxidation and aging of the glue.Wu Hao said that from a principle point of view, this is basically unsolvable. But for humanoid robot ankles, the long-term reliability of the six-dimensional force sensor is a core performance that cannot be compromised.
In addition, high rigidity and overload resistance are also the core performance tests to evaluate whether the six-dimensional force sensor can meet the core performance of humanoid robots.
The human ankle joint is an important load-bearing joint. Data shows that the load on the foot when walking is 1.5 times the body weight. Just like a human ankle, a humanoid robot's ankle needs to bear more than its own weight. Take the second-generation humanoid robot Optimus displayed by Tesla as an example. The humanoid robot is 1.8 meters tall and weighs 57KG.The corresponding weight that the ankle needs to bear may exceed 57KG.
As mentioned above, it is necessary to have high rigidity, strong overload resistance and temperature sensitivity drift control capabilities, as well as long-term reliability. So what technical route of six-dimensional force sensor is more suitable for humanoid robot applications than the strain gauge type?
Focusing on this issue, Ruima Sensor has launched research and development exploration on multiple technical routes, and has achieved results. Recently, it has launched two series of six-dimensional force sensor products in different directions, namely piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensors and MEMS principle joint torque sensor.
Piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor
More suitable for humanoid robot ankle application requirements
The characteristics of the piezoelectric technology route are: high rigidity, high sensitivity, no zero drift, not affected by temperature changes, and theoretically unlimited service life. The piezoelectric type does not require an external power supply or glue bonding process, and does not have problems such as oxidation and aging of the glue of the strain gauge type.
Due to the high technical difficulty of piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensors, the current market applications are still dominated by foreign brands such as Swiss Kistler. In contrast, in China, most companies have not yet deployed, or are in the research and development, verification and other stages. Today, Ruima Sensor has broken through this technology and achieved self-development and production of piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensors.
The piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor developed by Ruima Sensor adopts the principle of piezoelectric quartz crystal. It is a pre-loaded six-dimensional force sensor that can be used to measure forces (Fx, Fy, Fz) and torques in three orthogonal directions. (Mx, My, Mz), all direction force and torque signals are sensed and output by individual piezoelectric crystals.
The piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor launched by Ruima Sensor has high rigidity, high stability, low temperature drift, low zero drift, good long-term reliability, strong overload resistance (≤120%), wide operating temperature range, and long service life. It has the advantages of high natural frequency, upper and lower double flange connection, extremely low threshold, service life of over 100 million times, and high IP rating, which is more suitable for the application needs of humanoid robot ankles.
Specifically, the product's temperature sensitivity drift (≤0.05%F.S/℃) performs better than the strain gauge type, and has a wider operating temperature range (-40-120℃), which is especially suitable for general-purpose humanoid robot applications. In addition, in terms of product design, Ruima Sensor's piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor has a compact structure and can complete dynamic or quasi-static measurement of force/torque even in a very small space.
Regarding its rigidity and sensitivity, Wu Hao gave an example: "The piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor can balance rigidity and sensitivity very well. It can not only accurately measure the weight of the truck, but also distinguish the weight of the chewing gum spit out by the driver. "
For dynamic force testing applications, quartz piezoelectric load cells have many advantages and unique characteristics, making them the best choice for dynamic force measurement. However, its pressure-holding performance is not good, and its ability to measure static force is slightly insufficient.
The measurement signal generated by the quartz piezoelectric load cell will attenuate with time and is not suitable for long-term, static measurements. Therefore, it cannot be used for interchange of strain gauge load cells for static measurement. To give a common example: when ten weights are placed, the piezoelectric sensor can measure immediately, but it cannot measure after a period of time. In addition, the accuracy of piezoelectric force sensors is not as high as that of strain gauges.
"But these two deficiencies do not affect its application in humanoid robots. Theoretically, humanoid robots are constantly moving and measure dynamic forces. In addition, humanoid robots have requirements for six-dimensional force sensors. The main thing is repeatability and long-term stability, not how high the accuracy is." Wu Hao said.
MEMS principle joint torque sensor
Suitable for collaborative robots and humanoid robots
In addition to piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensors, Ruima Sensor has also developed MEMS principle joint torque sensors based on MEMS silicon principles suitable for collaborative robots and humanoid robots.
It is reported that the MEMS principle joint torque sensor developed by Ruima Sensor has high rigidity, strong impact resistance, small zero point drift, strong bending moment resistance, good forward and reverse symmetry, is affected by radial force, and has a high physical bandwidth of more than 1000HZ. Full temperature range compensation, higher sensitivity and other features.
Taken together, this torque sensor can adapt to robot collisions, jumps and other impacts without damaging the sensor or producing zero point drift. It can realize automated production and make product quality, reliability and consistency more reliable.
"Making customers more assured, secure and safer, the MEMS principle joint torque sensor is extremely cost-effective and is conducive to early mass production in the humanoid robot industry," Wu Hao said. In addition, it has a unique self-compensation technology for cross-load effects, which makes the impact of cross-loads on the torque signal small.
This MEMS principle joint torque sensor also does not require glue and uses silicon micro-melting technology. And like the piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor, it has outstanding performance in overload capacity, temperature sensitivity drift, long-term reliability, rigidity, consistency, etc.
Wu Hao even bluntly said that the MEMS principle joint torque sensor using this technical route is 10 times better than the strain gauge type in many performances, especially the sensitivity is 20 times that of the strain gauge type.
There are two six-dimensional force sensor solutions commonly used in collaborative robots. One is installed at the end of the collaborative arm; the other is installed at each joint. Each joint requires one joint torque sensor, and a collaborative robot requires a total of 6 or 7, depending on the number of joints.
For humanoid robots, the number of MEMS principle joint torque sensors required depends on the design of the body itself. Taking the second-generation humanoid robot Optimus displayed by Tesla as an example, it has a total of 40 joints, each joint is equipped with a torque sensor, and a total of 40 MEMS principle joint torque sensors are required.
From a production perspective, according to Wu Hao, the MEMS principle joint torque sensor of this technical route has high requirements for automated production, so the cost of equipment and production lines required in the early stage is relatively high. But from another point of view, when the volume is increased and it enters large-scale production, the cost of the product will be lower than that of the strain gauge type.
"The new MEMS principle torque sensor will be released soon. After rigorous testing and optimization, this revolutionary new sensor uses the MEMS principle as the basis to innovatively improve the torque measurement solution, thereby achieving high accuracy and high efficiency. In our efforts to innovate. At the same time, we maintain our commitment to quality and provide products that best suit customer needs." Wu Hao said.
Looking at the "human figure" from afar, waiting for the wind to come, and doing practical things down-to-earth
In the field of humanoid robots, Ruima Sensors has already laid out its plans. Not only has it developed corresponding products, but it has also been cooperating with many leading humanoid robot companies in the industry. It is worth mentioning that Ruima sensors have achieved fully automated production and can achieve batch delivery with guaranteed quality.
However, Wu Hao said that humanoid robots are only the company's long-term growth point in the next 5-10 years or even longer. The main growth points in the past three years will mainly come from the fields of industrial robots and collaborative robots, as well as the fields of welding and precision assembly.
Among them, in terms of collaborative robots, in 2023 Ruima sensors have successively provided prototypes to head manufacturers such as Han's Robot, Aobo Intelligent, Faaoyiwei, Changguangxi Intelligent, and Yuejiang Robot. It mainly cooperates with collaborative robots to perform drag-and-drop teaching on the welding process and complete welding trajectory planning.
In terms of product research and development, Ruima Sensors has always adhered to the "multi-technical route" innovative development. Wu Hao said that the company's R&D team is young and has strong learning ability. Taking the piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor as an example, it only took 6 months from development to implementation.
Currently, Ruima Sensor's six-dimensional force sensor products have a diameter span ranging from 9.5mm to 300mm, a force range span from 5N to 50KN, and a torque range span from 0.1N.m to 1000N.m, which can cover most application fields. Its product structures include hollow type, flange type, IP68 waterproof, miniature type, self-contained fastening screw type, etc., covering almost all structures of conventional six-dimensional force sensors.
In terms of product research and development, Ruima Sensors has always adhered to the "multi-technical route" innovative development. Wu Hao said that the company's R&D team is young and has strong learning ability. Taking the piezoelectric six-dimensional force sensor as an For example, it only took 6 months from development to implementation.
On April 18, 2024, Ruima Sensor will participate in the 2024 China Humanoid Robot Technology Application Summit held by Gaogong Mobile Robot and Gaogong Robot Industry Research Institute (GGII), and as a participating unit, jointly witness the "Humanoid Robot Industry" The launch ceremony of the Development Blue Book.